Artichoke (Cynara scolymus) is a native plant of the Mediterranean (North Africa and Southern Europe) and is commonly known as artichoke in Brazil. Artichoke is cultivated worldwide due to its benefits and medicinal properties.
Artichoke leaf extract was one of the few herbal remedies which the clinical and experimental trials have complemented each other. Specifically, it has antioxidant, choleretic, hepatoprotective, bile-enhancing, and lipid-lowering properties. These experimental and clinical effects have been verified through extensive biomedical herbal studies.
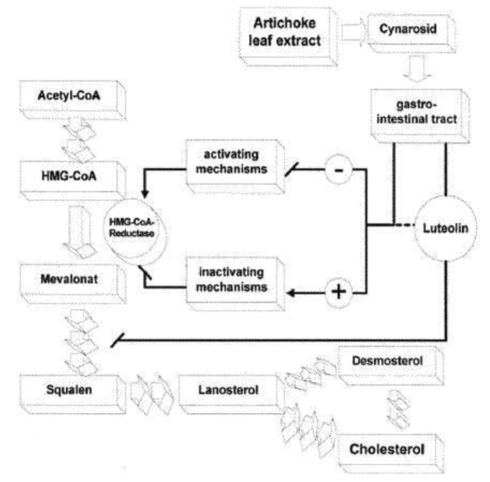
In animal studies, liquid extracts of the roots and leaves of artichoke have demonstrated the ability to protect the liver and may even help liver cells regenerate. It may also act as a cholesterol-lowering agent (as shown in the figure below), thus helping to prevent heart disease. Boiled wild artichoke reduced postprandial glycemic and insulinemic responses in normal subjects but had no effect on metabolic syndrome patients. The researchers also showed a significant reduction in the levels of biological parameters in hematological tests, biochemistry (glucose levels, cholesterol rates, and the atherosclerotic index), and cardiovascular disorders.
Human studies have shown that artichoke leaf extract is one of the safest herbal drugs, with almost no adverse effects in most subjects, although its full safety testing has not yet been completed.
In conclusion, as a nutritional supplement and antioxidant, artichoke leaf extract could safely be used as an adjunct to conventional therapies.
Salem, M. B., Affes, H., Ksouda, K., Dhouibi, R., Sahnoun, Z., Hammami, S., & Zeghal, K. M. (2015). Pharmacological studies of artichoke leaf extract and their health benefits. Plant foods for human nutrition, 70, 441-453. [Link]