Maitake (Grifola frondosa) is an edible mushroom. The water-soluble extract of Maitake mushrooms has been confirmed to contain substances with antidiabetic activity. The MD-fraction containing a ß-glucan extracted from Maitake has been analyzed for various medicinal properties, such as antitumor, antihyperlipidemic, and anti-hepatitis effects. It is also increasingly believed that the MD fraction strongly enhances the activity of immunologically active cells. These reports suggest that some of the components of the Maitake mushroom extract may represent potential cancer-chemopreventive substances.
Therefore, scientists investigated the effects of water-soluble Maitake extract on cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis in four human gastric cancer cell lines (TMK-1, MKN28, MKN45, and MKN74). The results revealed that Maitake extract (ME) inhibited proliferation in a time-dependent manner in all four cell lines (as shown below). This inhibition was most pronounced in TMK-1 cells, which exhibited up to 90% inhibition after 3 days of treatment with 10% ME. After investigating its inhibitory pathway, it was discovered that ME induces apoptosis in TMK-1 cells via caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways, potentially resulting in an antitumor effect on gastric cancer.
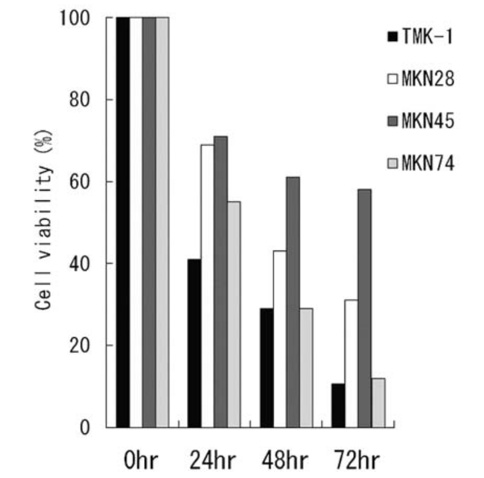
Note: ME induces cell death in a time-dependent manner in all four cell lines. The data shown are the means of three independent experiments.
Shomori, K., Yamamoto, M., Arifuku, I., Teramachi, K., & Ito, H. (2009). Antitumor effects of a water-soluble extract from Maitake (Grifola frondosa) on human gastric cancer cell lines. Oncology reports, 22(3), 615-620. [Link]