Chronic high-fat (HF) dietary intake can cause neuroinflammation and cognitive decline via the gut-brain axis. (1, 3) / (1, 6)-β-glucan, an edible polysaccharide isolated from Shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes), has the potential to reshape the gut microbiota. However, the effects of L. edodes derived β-glucan on HF diet-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive decline remain unknown, so researchers explored experimentally the neuroprotective effects and mechanisms of L. edodes β-glucan supplementation on obesity-associated cognitive decline in mice fed by a HF diet.
The results found that short-term and long-term supplementation with L. edodes β-glucan prevented the shifts in gut microbial composition induced by the HF diet. Long-term supplementation with L. edodes β-glucan prevented HF diet-induced recognition memory impairment, which was assessed by behavioral tests (the temporal order memory, novel object recognition and Y‐maze tests) (as shown in the figure below). In the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, L. edodes β-glucan supplementation ameliorated HF diet-induced alterations in synaptic ultrastructure, neuroinflammation and deficits in brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). In addition, supplementation with L. edodes β-glucan increased mucosal thickness, upregulated the expression of the tight junction protein occludin, thereby reducing plasma lipopolysaccharide levels, and inhibited proinflammatory macrophage accumulation in the colon of mice fed by HF diet.
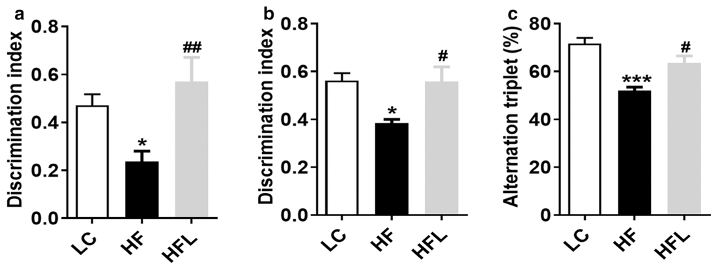
Note: a Discrimination index in the temporal order memory test, b discrimination index in the novel object recognition test, c proportion of correct alternations in the Y-maze test. n= 10 per group. Data are presented as mean ±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, vs lab chow diet group (LC); #P <0.05, ##P<0.01, vs high-fat diet group (HF). HFL, L. edodes ß-glucan supplementation in HF diet group.
This finding suggests that dietary L. edodes β-glucan supplementation may be an effective nutritional strategy to prevent HF diet-induced cognitive deficits with improvement in the gut-brain axis.
Pan, W., Jiang, P., Zhao, J., Shi, H., Zhang, P., Yang, X., … & Yu, Y. (2021). β-Glucan from Lentinula edodes prevents cognitive impairments in high-fat diet-induced obese mice: Involvement of colon-brain axis. Journal of Translational Medicine, 19, 1-17. [Link]