Cynara scolymus L. (common artichoke) and its products have been considered potential herbal remedies for a variety of conditions, including cardiovascular disease, liver disease, and gastric disorders. Until now, the effects of artichoke and its products administration on glycemic indices have not been sufficiently appraised.
The researchers, therefore, evaluated the artichoke and its products administration on the glycemic index. Data obtained from nine RCTs with 512 participants (275 cases and 237 control) were used for this meta-analysis.
Results showed that a pooled analysis of nine randomized controlled trials (RCTs) showed that the administration of artichoke and its products resulted in a significant reduction in fasting blood sugar (FBS). However, other glycemic indices including fasting insulin, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), or Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), did not change after administration of artichoke and its products (as shown in the figure below). A subgroup analysis comparing the kind of intervention revealed that the supplementation of artichoke and artichoke products alone, in a noco-supplementation form, was efficacy for the reduction of the Homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR).
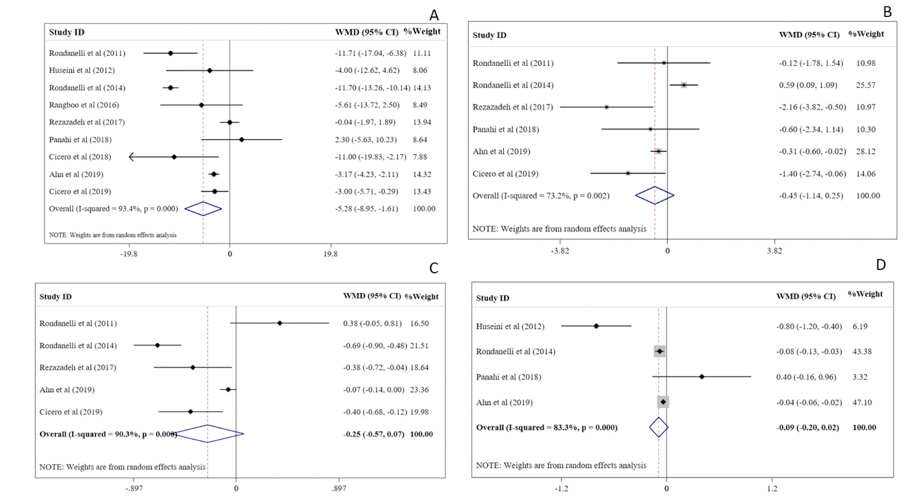
In conclusion, the supplementation of artichoke and its products was effective in reducing FBS concentrations in humans. Moreover, the results showed that the administration of artichoke and its products alone is more effective in the reduction of HOMA-IR levels than the co-supplementation form.
Jalili, C., Moradi, S., Babaei, A., Boozari, B., Asbaghi, O., Lazaridi, A. V., Hojjati Kermani, M. A., & Miraghajani, M. (2020). Effects of Cynara scolymus L. on glycemic indices:A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complementary therapies in medicine, 52, 102496. [Link]