Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common liver diseases in developed countries, and in addition, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is caused by increased oxidative stress, hepatocyte inflammation, and insulin resistance. Treatment of this disease can be done through weight loss, changes in dietary composition, and lifestyle modifications. Among these, herbal substances have always received a lot of attention as an alternative approach to treating chronic diseases such as NASH.
According to some evidence, one of the plants used for the protection of hepatocytes is the artichoke (Cynara scolymus). It has a high concentration of natural antioxidants and also has antibacterial and cholesterol-lowering properties. It may have a protective effect against NAFLD by reducing the production of reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation, and protein oxidation, as well as increasing the activity of glutathione peroxidase.
Thus far, researchers have assessed the effects of artichoke administration on liver enzymes by reviewing the literature and conducting a meta-analysis. As a result, a pooled analysis of seven randomized controlled trials (RCTs) showed that artichoke administration had an effect on both alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (results shown below). A greater effect on ALT was detected in trials lasting ≤8 weeks. In addition, a greater effect on AST was detected in trials using >500 mg of artichoke. Overall, this meta-analysis showed that artichoke supplementation decreased ALT and AST.
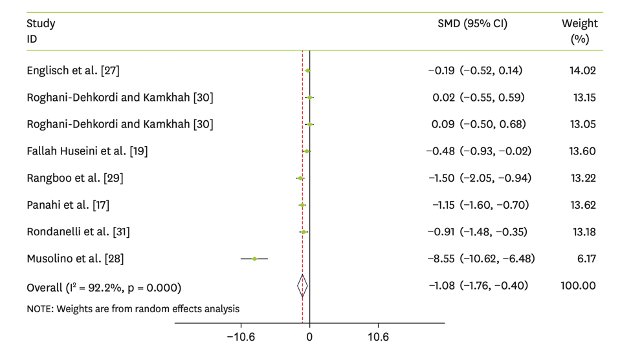
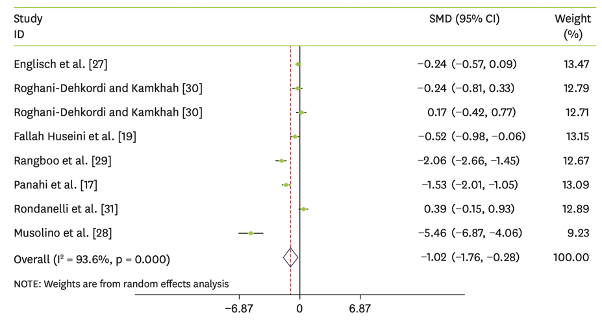
Note: SMD, standardized mean difference; CI, confidence interval.
In conclusion, this systematic review and meta-analysis of intervention trials suggests that artichoke supplementation may reduce serum levels of AST and ALT. The results of this study may also provide additional evidence for physicians and medical researchers regarding the efficacy of alternative therapies for hepatic patients.
Amini, M. R., Sheikhhossein, F., Talebyan, A., Bazshahi, E., Djafari, F., & Hekmatdoost, A. (2022). Effects of Artichoke Supplementation on Liver Enzymes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clinical Nutrition Research, 11(3), 228. [Link]