Fundamentally, high blood pressure (BP) is considered an important leading global cause of a range of diseases, namely heart failure, heart attacks, stroke, renal dysfunction, dementia, and all-cause mortality. Preventing, monitoring, or managing hypertension, especially in the primary stages, can help to reduce the risk of its subsequent disease and burden of treatment. And lifestyle changes and medicinal agents are preferred methods of managing and treating hypertension.
Among them, artichoke is a sunflower species belonging to the Asteraceae family. Clinical trials have shown that extracts from artichoke may have the ability to treat several diseases, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), hypocholesteremia, metabolic syndrome, and hypertension.
Researchers searched the Cochrane Library, PubMed, Embase, and Scopus databases to find relevant studies (as shown in the figure below) and performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the effects of artichoke administration on blood pressure.
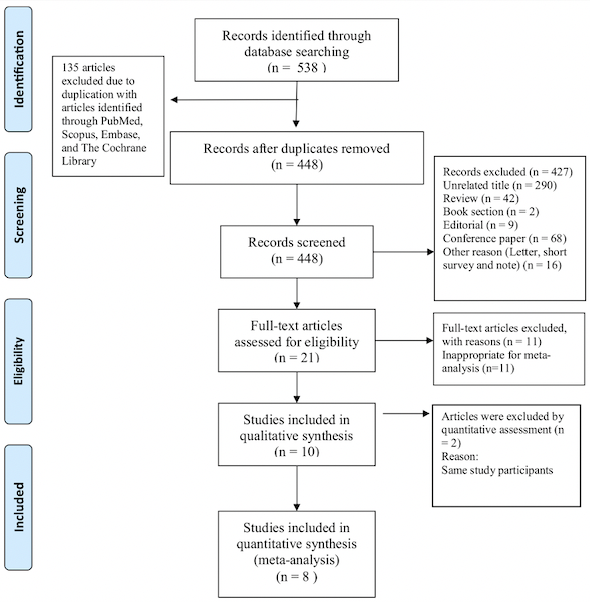
A pooled analysis of eight randomized controlled trials showed that artichoke supplementation did not have an effect on systolic blood pressure (SBP), or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) when compared to the placebo group. However, a subgroup analysis based on health status suggested that artichoke administration may significantly reduce SBP and DBP in patients with hypertension, but no such reduction was found in patients with NAFLD. Furthermore, our results suggest that artichoke supplementation for 12 weeks resulted in a significant decrease in DBP, but not for the 8-week intervention.
In conclusion, artichoke supplementation may potentially lead to cause a decrease in SBP and DBP in hypertensive patients. In addition, artichoke supplementation for 12 weeks significantly improved DBP.
Moradi, M., Sohrabi, G., Golbidi, M., Yarmohammadi, S., Hemati, N., Campbell, M. S., … & Farzaei, M. H. (2021). Effects of artichoke on blood pressure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 57, 102668. [Link]