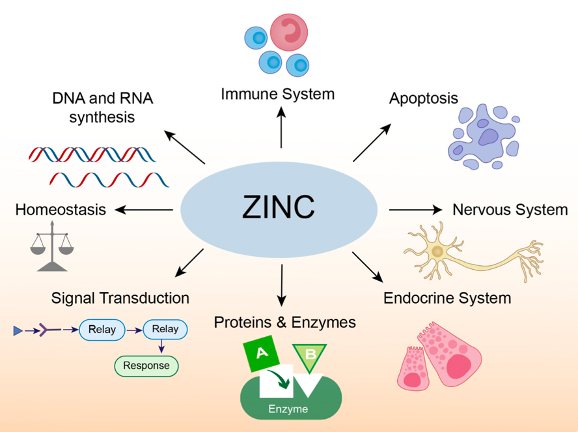
Zinc is a trace element essential for human survival, and its physiological roles in cells and organs are shown in the figure below. Its deficiency has been associated with various adverse effects, such as growth retardation, impaired immune system function, and cognitive dysfunction. Zinc is implicated in the synthesis and activity of many proteins and enzymes, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) polymerases, and insulin.
Zinc is also one of the most abundant metal ions in the central nervous system, and a major site of storage of zinc is the telencephalon, particularly in the cortical areas, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Zinc plays a role in both physiological and pathological processes in the central nervous system. From neonatal brain development to the preservation and control of adult brain function, zinc is a vital homeostatic component of the central nervous system. Neurogenesis is particularly robust during the embryonic and neonatal periods. During neurodevelopment, zinc plays a key role in neuronal proliferation and differentiation, neuronal migration, and axonal growth. During development and in adulthood, zinc acts as a regulator of synaptic activity and neuronal plasticity at the cellular level. Several neurological disorders, namely stroke, neurodegenerative diseases, traumatic brain injury, and depression, may also be affected by changes in zinc status.
Zinc deficiency may result in declines in cognition and learning and an increase in oxidative stress, while zinc accumulation may lead to neurotoxicity and neuronal cell death. Zinc deficiency is commonly caused by inadequate dietary intake, whereas abnormal zinc accumulation is associated with the inhibition of zinc transporters or activation of oxidative stress. Hence, zinc homeostasis and its regulation may affect a wide range of molecular functions and pathological outcomes, and different environmental and dietary habits and ecological conditions may influence zinc homeostasis. Thus, maintaining zinc homeostasis is essential for brain health.
Li, Z., Liu, Y., Wei, R., Yong, V. W., & Xue, M. (2022). The Important Role of Zinc in Neurological Diseases. Biomolecules, 13(1), 28. [Link]