Artemisia absinthium L. is a large and diverse genus of the family Asteraceae. It has been used worldwide as a customary herbal medicine to treat gastric pain, cardiac stimulation, improvement of memory and for the restoration of declined mental function.
The liver is an important target for drug and xenobiotic toxicity. The imbalance between endogenous antioxidant defense system and reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in the body leads to oxidative stress, which is associated with the overproduction of free radicals from various liver diseases, such as alcoholic liver injury, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and drug-induced liver injury. Recently, natural agents with improved effectiveness and safety profiles have been widely sought as a treatment for liver diseases.
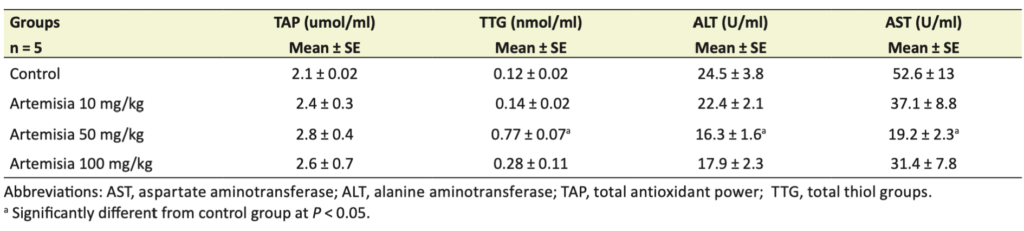
Therefore, researchers experimentally evaluated the hepatoprotective effects of Artemisia absinthium on a number of factors reflecting the development of oxidative toxic stress in plasma. During the experiment, they divided 20 male rats equally into 4 groups (5 rats in each group). Group I was the control group and was gavaged with normal salin. 3 treatment groups (II, III, IV) were gavaged with Artemisia absinthium 10, 50 and 100 mg/kg/day, respectively. After treatment, blood specimens were collected and their liver enzymes, such as aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), as well as total antioxidant power (TAP) and total thiol groups (TTG) concentrations were measured. The results of the experiment are shown in the table below, the levels of ALT and AST decreased in the group II compared to the control group (group I). The ALT and AST were significantly decreased in the Artemisia absinthium 50 mg/kg group compared to the control group. Also, TTG was increased in the Artemisia absinthium 50 mg/kg group compared to the control group.
In conclusion, the experiment demonstrated that Artemisia absinthium could exert its antioxidant or free radical scavenging activity, thus preventing the formation of ROS. Artemisia absinthium is able to ameliorate liver toxicity by reducing oxidative damage and might be beneficial in patients using toxic agents.
Mohammadian, A., Moradkhani, S., Ataei, S., Shayesteh, T. H., Sedaghat, M., Kheiripour, N., & Ranjbar, A. J. J. H. P. (2016). Antioxidative and hepatoprotective effects of hydroalcoholic extract of Artemisia absinthium L. in rat. J HerbMed Pharmacol, 5(1), 29-32. [Link]