Pollution has merged into our everyday lives along with the rise of heavy industry, industrial progress, and people’s quality of life.
There are heavy metals everywhere, including those that are often found in the environment like zinc, copper, and iron as well as color-changing metals like lead, arsenic, mercury, and cadmium. The harmful consequences of heavy metals on human health have received a lot of attention recently.
Among these, cadmium may seriously harm a number of important organs as well as the neurological, reproductive, and immunological systems when it enters the human body. Additionally, it has a potently harmful impact on cells. Short-term exposure to cadmium can cause apoptosis and necrosis, and long-term exposure can induce cancer cells and lead to tumors.
Through a review of the literature, the researcher summarized the available evidence on how cadmium exposure affects health, elucidating the effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the immune system. By analyzing the general manifestations of inflammation caused by cadmium exposure, it was also found that omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids act in vivo to counteract the damage caused by cadmium (as shown in the figure below).
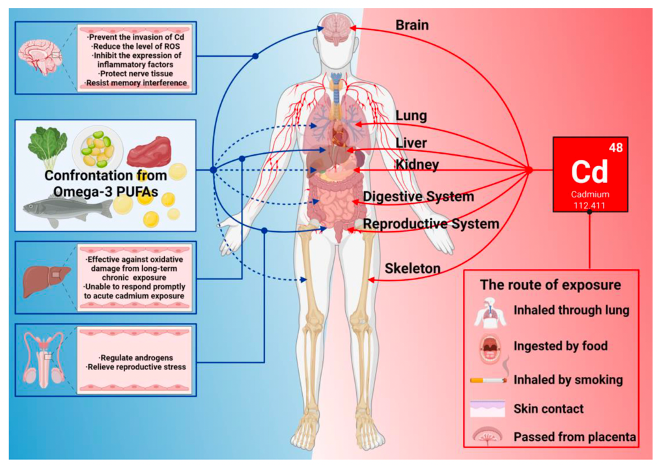
Overall, although it remains to be verified whether omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids can be used as therapeutic agents, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation is reliable and effective as a rehabilitation therapy.
Chen, Z., Lu, Q., Wang, J., Cao, X., Wang, K., Wang, Y., … & Yang, Z. (2022). The function of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in response to cadmium exposure. Frontiers in Immunology, 13. [Link]
Kim, J. J., Kim, Y. S., & Kumar, V. (2019). Heavy metal toxicity: An update of chelating therapeutic strategies. Journal of Trace elements in Medicine and Biology, 54, 226-231. [Link]
Fu, J., Liu, K., Du, W., Wang, Z., Li, S., & Du, X. (2017, March). Microstructure and mechanical properties of the as-cast Mg-Zn-Mn-Ca alloys. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 182, No. 1, p. 012053). IOP Publishing. [Link]