Acne is one of the most common skin conditions and is influenced by many genetic and hormonal factors. It is most common in adolescents but may involve people of all ages. Although effective treatment options can be found, acne can also be difficult to cure.
Several studies have shown that nutrition is one of the key factors involved in the pathogenesis of acne. This review summarizes the current biological links between acne and diet, with a particular focus on the most frequently discussed factors involved in its pathogenesis: milk, chocolate, omega-3 fatty acids, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinism, and IGF-1.
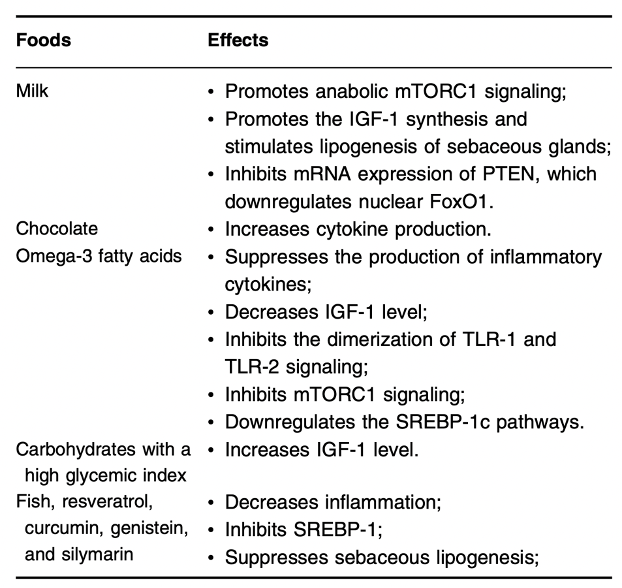
In the table below, the different types of foods and their influence on the pathogenesis of acne are first described. Moreover, data from some experiments show that a diet with a high glycemic index may be a trigger in acne pathogenesis, while patients on a low glycemic index diet have fewer acne lesions. Milk and chocolate have also been associated with the exacerbation of acne. However, foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids can inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines and have a therapeutic effect on acne.
Conforti, C., Agozzino, M., Emendato, G., Fai, A., Fichera, F., Marangi, G. F., … & Dianzani, C. (2022). Acne and diet: a review. International Journal of Dermatology, 61(8), 930-934. [Link]